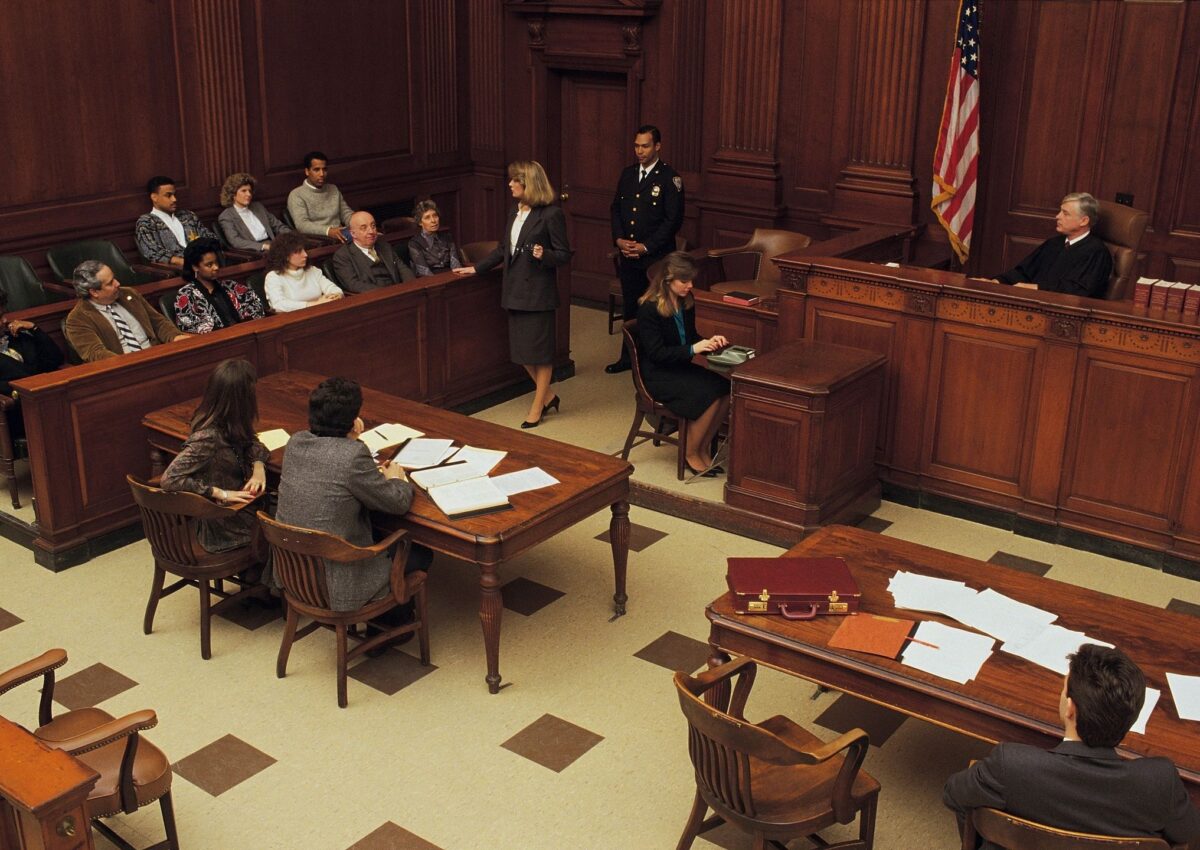
Vicarious liability in California refers to the legal principle where one party is held responsible for the actions or omissions of another, typically within the context of an employer-employee relationship. Under California law, an employer can be held liable for the negligent or wrongful acts of an employee that occur within the scope of employment. This means if an employee causes harm or injury while performing job-related duties, the employer may be required to pay damages, even if the employer was not directly at fault. The rationale behind vicarious liability is to ensure that victims of harm have a more accessible party (often the employer) to pursue for compensation, as employers are typically better able to bear financial responsibility.
However, there are limitations to vicarious liability in California. The key requirement is that the employee’s actions must occur within the “scope of employment,” meaning they must be related to the duties the employee was hired to perform. If an employee’s actions are considered “frolics” or personal endeavors unrelated to work, the employer may not be held liable. For example, if an employee causes an accident while driving to a personal event, the employer would likely not be liable. The scope of employment test requires a careful analysis of whether the employee’s actions were incidental to their job duties or completely outside of their work responsibilities.
Visit: https://inlandempirelitigation.com/
Law Offices of James R. Dickinson – 909-848-8448
How To Schedule A Consultation:
Please call us at 909-848-8448 to schedule a free consultation/case evaluation or complete the form immediately below. [Please note certain formalities must be completed to retain the Law Offices of James R. Dickinson, such as the signing of a legal fee agreement [see “Disclaimers”]].